Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd. (SSTL) and partner the National Oceanography Centre (NOC) have released new datasets that demonstrate how reflections of satellite navigation signals collected in space can be used to accurately map the extent of the sea ice in the Arctic and Antarctic.
The measurements were taken by an SSTL smallsat called TechDemoSat-1 that was launched in 2014. The smallsat carried the SGR-ReSI, an instrument designed to demonstrate accurate measurement of ocean wind speeds around the globe using GNSS reflectometry.
The innovative new datasets use reflected Navigation signals from small satellite TechDemoSat-1.
Chart is courtesy of SSTL.
With funding from ESA, NOC developed the algorithms to estimate the wind speed from GNSS reflections, and recently added the capability to discriminate between ocean and ice. By exploiting the way that GNSS signals are used as radar sources it is believed that the ice edges can be detected with a higher resolution than using passive sensing methods, and this information is potentially valuable for shipping and off-shore energy, as well as climate and polar ice research.
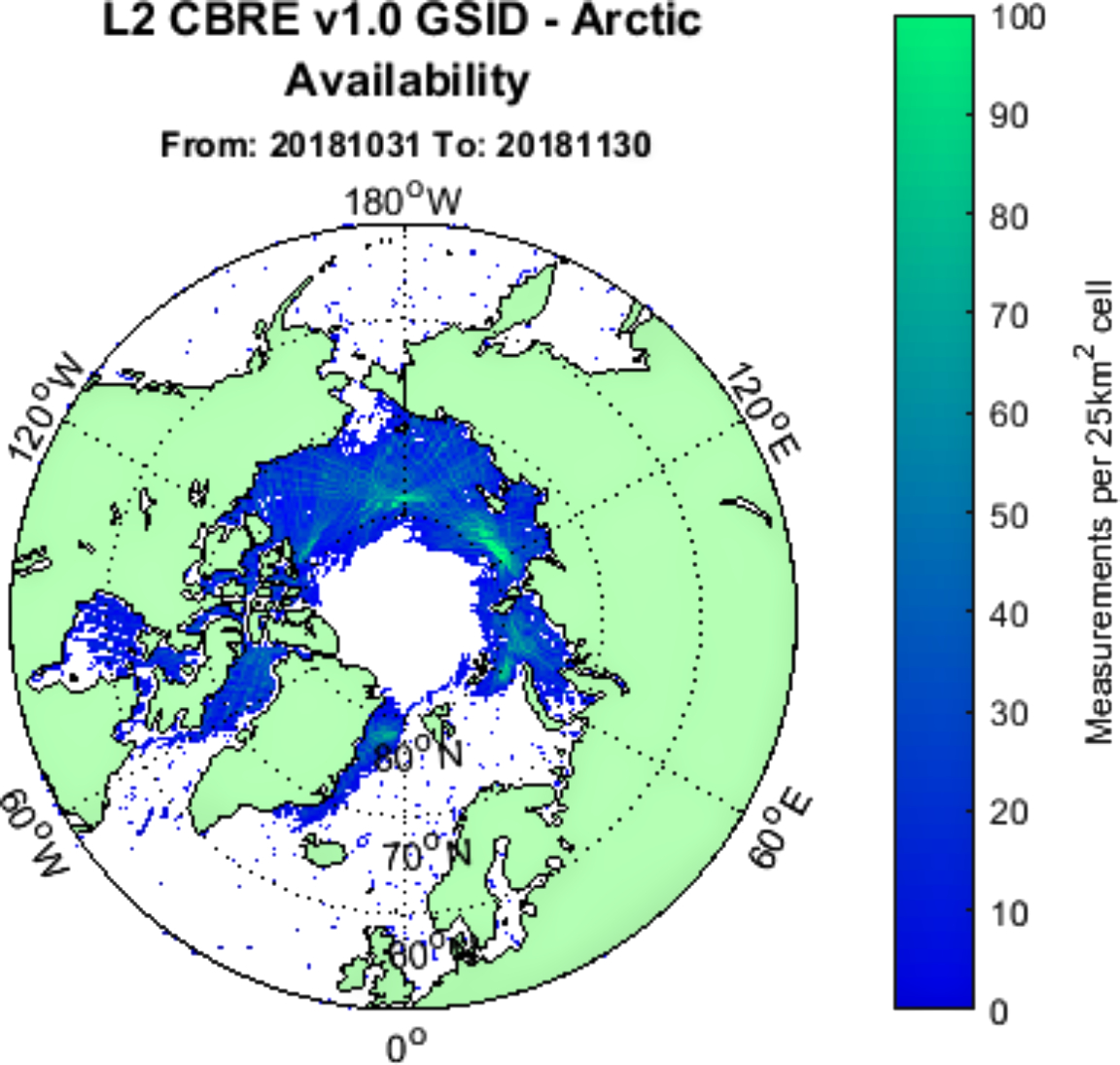
Images show the sea ice extent during November 2018 over the Arctic and Antarctic. The hole over the North Pole shows the high latitude limit of the TechDemoSat-1 satellite’s ability to collect GPS satellite reflections. The full set of Sea Ice detection data is available free of charge from data portal www.merrbys.co.uk.
The SGR-ReSI instrument from SSTL is flying on the 8-satellite NASA CYGNSS mission that was launched in 2016 to enable the measurement of hurricanes. The sensor can be carried on a smallsate and a future constellation could offer low delay, high accuracy ice edge mapping, in addition to the other benefits GNSS reflectometry brings over land, ice and ocean.

Artistic rendition of SSTl’s TechDemoSat-1 smallsat.
SSTL is working on a number of projects to exploit GNSS reflectometry for different applications and the SSTL HydroGNSS concept for sensing land hydrographic climate variables using GNSS reflectometry has recently been down-selected for the ESA Scout mission opportunity.
Phil Brownnett, Managing Director of SSTL, said that this is another important demonstration of the benefits of GNSS-Reflectometry for both commercial and scientific communities. SSTL, in collaboration with partners, has taken this new technique from feasibility to a world-leading capability which will see new missions uncovering further applications over ocean, ice and land.
Giuseppe Foti, Senior Scientist of NOC, added that these recent results show how collaboration between academia and industry is critically important to improve our understanding of ocean and ice processes that have a global impact on our planet.