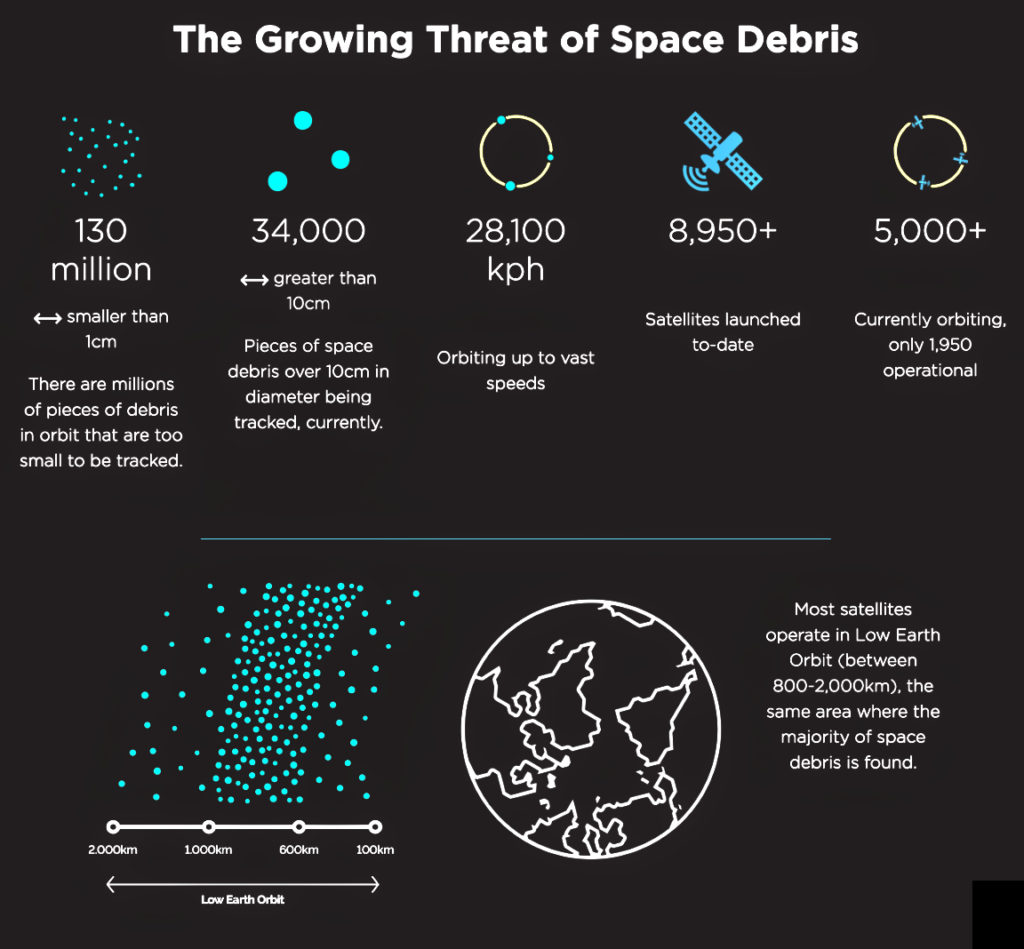
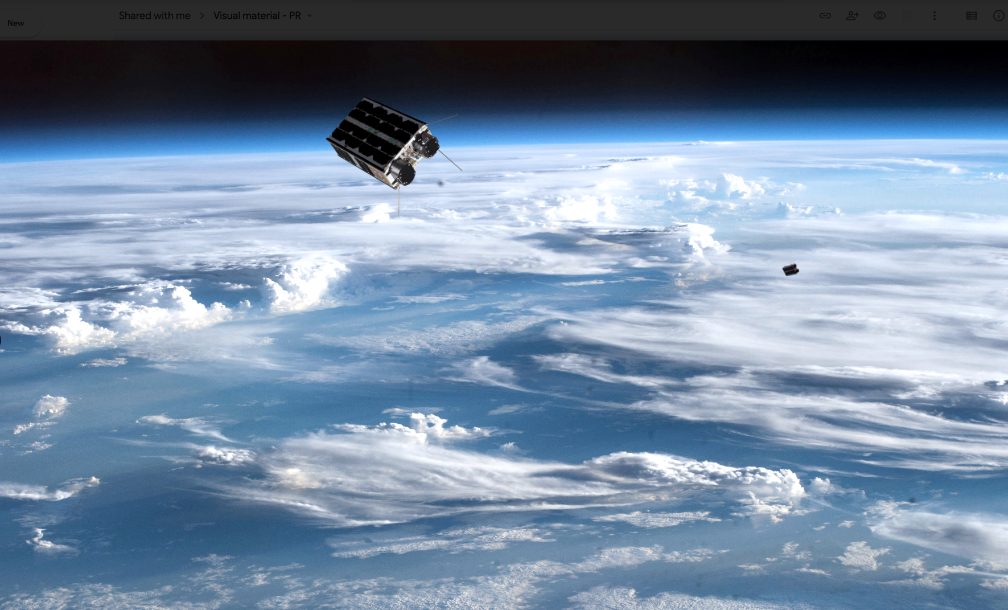
The Swedish government has made the decision to establish the capability to launch smallsats from the Esrange Space Center in northern Sweden.
This announcement is the third step in an extensive modernization of the infrastructure at Esrange to meet the growing demand of testing and launching capability in the space sector. Swedish Space Minister Matilda Ernkrans announced this decision during the inauguration of a new testbed facility for next generation rocket technology at Esrange.
Esrange Space center is already one of the most active and versatile launch sites in the world and the latest decision allows SSC to proceed with its goal to be able to launch small satellites into orbit by 2022.
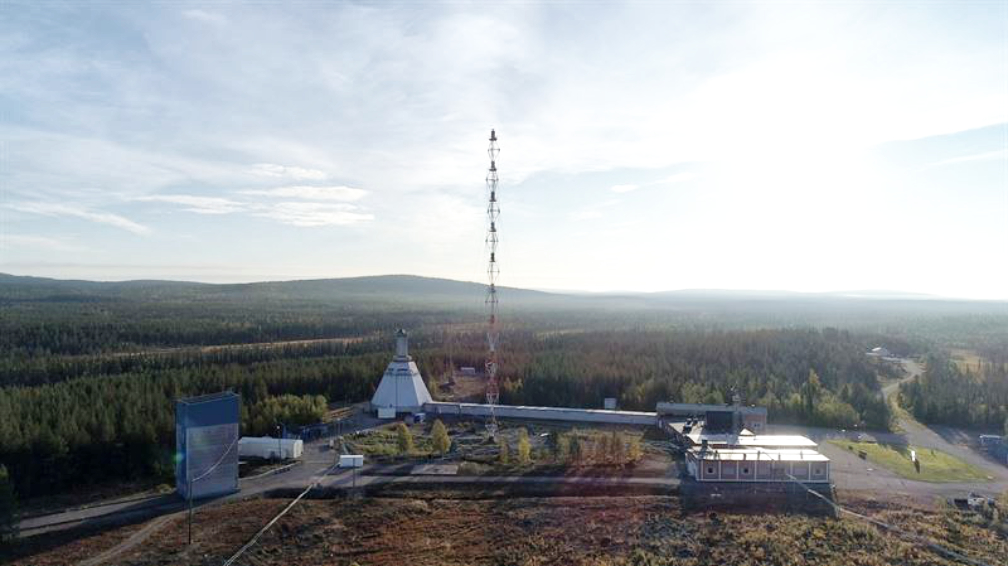

The announcement follows the overall ambition defined in the Swedish space strategy decided upon in 2018. The strategy underlines the importance of further developing Esrange in order to fully use its potential, strengthening Sweden’s position as a prominent space nation within the European and global space sector.
The new testbed at Esrange provides a platform for European and global space sector to develop next generation rocket technologies. This will now be supplemented with additional infrastructure needed for launching small satellites from Esrange.
The first rockets tests will be conducted by ISAR and RFA later this autumn, both already established at the site. The European Space Agency’s reusability programme Themis will conduct its first reusability test flights in 2022 from Esrange, in a collaboration between SSC and ArianeGroup supported by ArianeWorks (an innovation unit formed up by the French Space Agency CNES and ArianeGroup). SSC’s ambition is to launch the first satellites in 2022.
Executive Comments

“This means that Sweden will be one of the very few countries with capability to launch small satellites. We are very proud of having taken this decision,” said the Swedish Space Minister during her visit to Esrange.

“We are pleased that the Swedish government has now decided to establish the capability to launch satellites from Esrange. The decision means that Sweden will become a launching state, providing a capability that only a few countries have, of great importance for research, technology development and expanded international collaboration,” said Stefan Gardefjord, CEO at SSC.
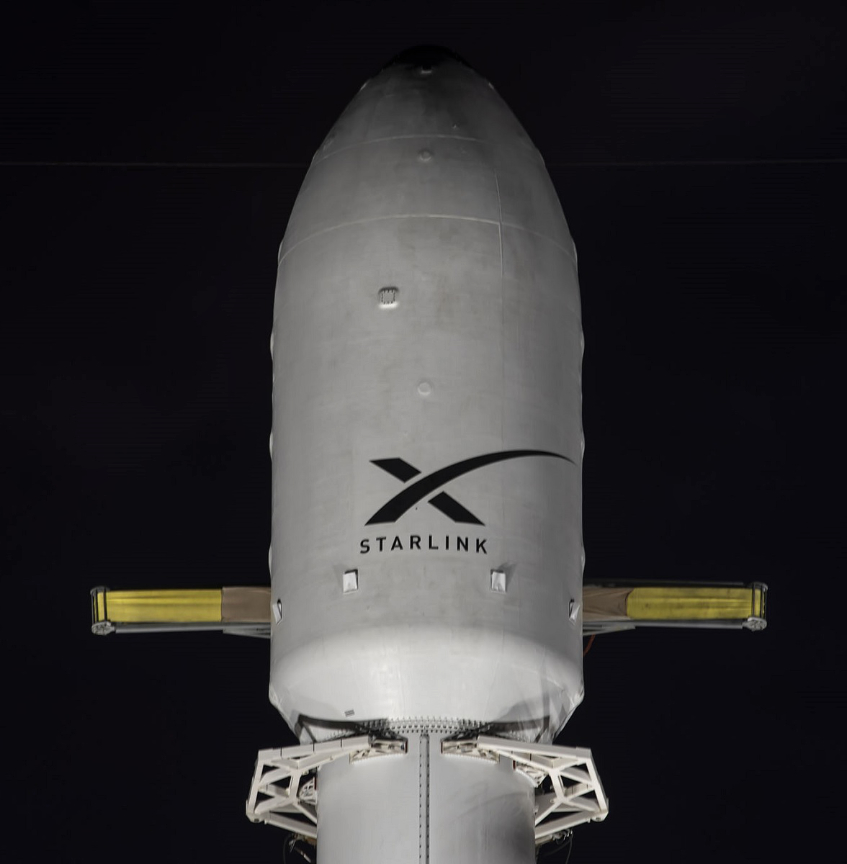








 Elon Musk’s satellite constellation
Elon Musk’s satellite constellation 
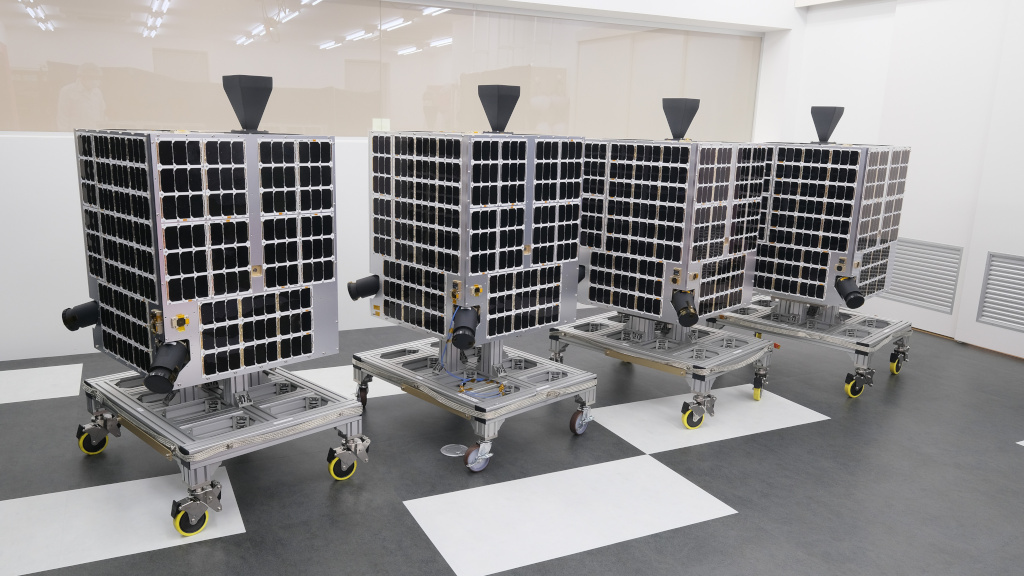






 The significant investment raised since its founding in 2013 has allowed Astroscale to establish a global footprint across five countries and grow to over 140 team members. Each of the five global offices are working in concert to achieve the Astroscale mission of safe and sustainable development of space for future generations.
The significant investment raised since its founding in 2013 has allowed Astroscale to establish a global footprint across five countries and grow to over 140 team members. Each of the five global offices are working in concert to achieve the Astroscale mission of safe and sustainable development of space for future generations.