Recently, Telesat Government Solutions, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Telesat (Nasdaq and TSX: TSAT), and ALL.SPACE announced a Memorandum of Understanding to integrate ALL.SPACE user terminals with the Telesat Lightspeed Low Earth Orbit (LEO) network.

Telesat Government Solutions will provide detailed Telesat Lightspeed network interface specifications to facilitate the development of ALL.SPACE multi-orbit, electronically steered terminals. The companies will collaborate on joint customer use-case evaluations and field demonstrations utilizing Telesat’s LEO 3 demonstration satellite. This collaboration is intended to ensure that ALL.SPACE terminals achieve type certification and are fully operational when Telesat Lightspeed services commence in late 2027.
Development efforts will include the ALL.SPACE Hydra-2 MAX terminal that maintains two simultaneous satellite connections with commercial and military Ka-band spacecraft across GEO, MEO and LEO orbits.
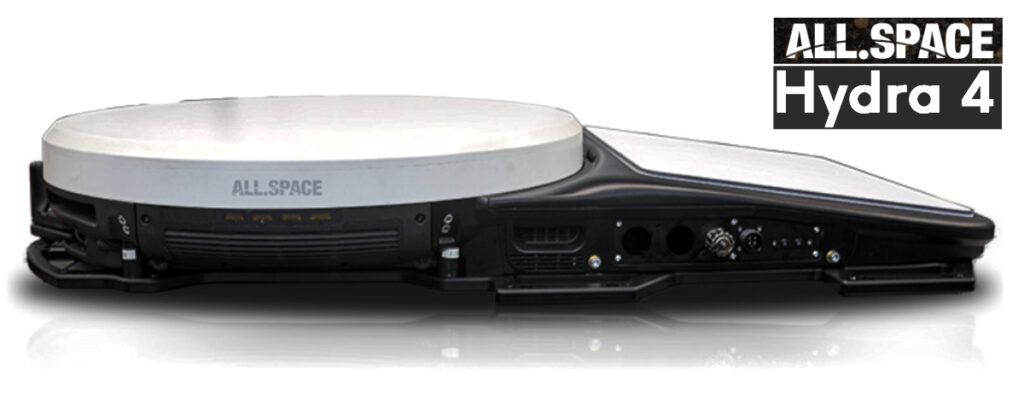
Additionally, the collaboration extends to the advanced Hydra-4 MAX MILSATCOM terminal that connects to four satellites simultaneously by combining a Hydra-2 MAX terminal, a Ku-band terminal and a global L-band antenna into a single chassis.
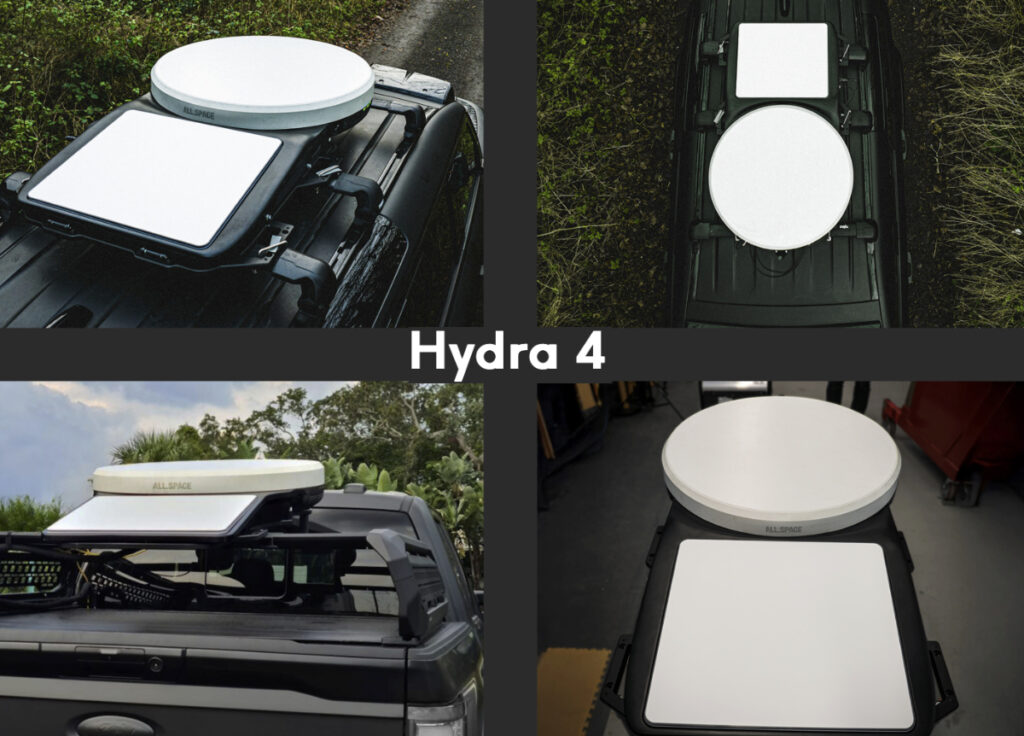

This important collaboration will ensure that Hydra 2 and Hydra 4 terminals that are deployed today, including those delivered to the U.S. Navy and U.S. Army, can seamlessly access Telesat Lightspeed in the future.
Chuck Cynamon, President of Telesat Government Solutions, said, “As the Department of Defense pursues proliferated architectures for assured connectivity, secure, ruggedized multi-band and multi-orbit terminals provide increased flexibility and resiliency in the congested and contested battlespace. The combination of our secure, advanced Telesat Lightspeed services and innovative ALL.SPACE terminals will increase operational advantage for the DoD in the digital battlespace.”
Paul McCarter, CEO of ALL.SPACE, said, “The future of resilient, global connectivity hinges on multi-orbit, multi-network architectures and our collaboration with Telesat marks a powerful step forward. Integrating our field-proven Hydra terminals with the advanced Telesat Lightspeed LEO capabilities will give government and defense users a critical operational edge – enabling seamless, secure, and scalable communications across every domain. This joint effort reflects our shared commitment to delivering the most agile and interoperable SATCOM solutions on the market.”