On January 28, 2026, the Government Accountability Office (GAO) released a critical report titled “Missile Warning Satellites: Space Development Agency Should Be More Realistic and Transparent About Risks to Capability Delivery” (GAO-26-107085).

The congressional watchdog warned that the Space Development Agency (SDA) is overestimating the technology readiness of critical elements within its Tracking Layer constellation, potentially jeopardizing its ability to field hypersonic missile defense capabilities on schedule.
Acting Director Dr. Gurpartap “GP” Sandhoo remains the official head of the Space Development Agency (SDA) as of January 28, 2026, and he is navigating a period of significant institutional pressure. This newly released Government Accountability Office (GAO) report (GAO-26-107085) has flagged critical risks in the agency’s flagship missile-tracking program, placing the SDA’s rapid acquisition model—and by extension, its current leadership—under intense federal oversight.
Technological Maturity and Contractor Delays
According to the GAO, the SDA’s current strategy of rapid, biennial “tranches” has led to unplanned work as contractors struggle to modify commercial spacecraft for specialized military missions. While the agency has reported achieving early milestones for the Proliferated Warfighter Space Architecture (PWSA), the GAO asserts these reports fail to reflect underlying schedule risks.
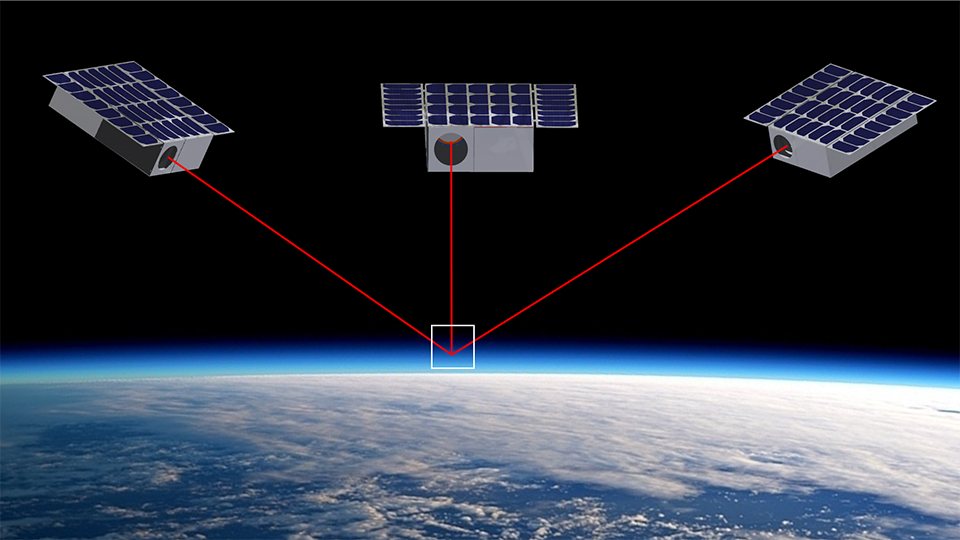
Perhaps most significantly, the report highlights that the SDA and its partners have yet to fully demonstrate the generation of timely, three-dimensional tracks on the ground—a baseline requirement for countering hypersonic glide vehicles.
Budgetary Scale and Contractual Scope
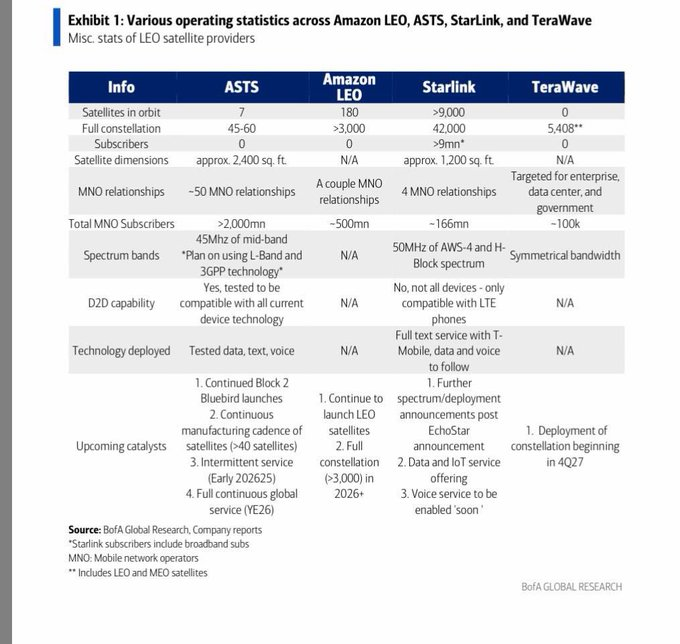
The Tracking Layer is a massive procurement effort aimed at deploying hundreds of satellites in Low Earth Orbit (LEO). As of January 2026:
- Total Investment: The PWSA is projected to cost nearly $35 billion through fiscal year 2029.
- Active Contracts: Over $4.7 billion has been awarded for the first 101 satellites.
- Key Primes: Major contractors including Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, and L3Harris are currently developing satellites for Tranches 1 and 2 of the Tracking Layer.
Criticism of the Requirements Process
The GAO report also flagged a lack of transparency between the SDA and the combatant commands that will ultimately use the data. Combatant commanders reported having “insufficient insight” into how the SDA defines requirements or whether the planned capabilities will meet operational needs for missile warning and tracking (MW/MT).
Under the leadership of Dr. Gurpartap “GP” Sandhoo, who assumed the role in September 2025, the agency has maintained its “constructive disruptor” status, awarding contracts every two years regardless of previous satellite performance. The GAO recommends moving toward an “architecture-level schedule” to better understand how delays in individual tranches impact the overall delivery of global missile defense.
Path Forward and Air Force Oversight
The GAO has recommended that the Secretary of the Air Force ensure the SDA follows a more collaborative process with warfighter participants to define and prioritize requirements. Additionally, the report urges the Department of Defense to create a reliable life-cycle cost estimate, noting that limited cost data was collected for Tranches 1 and 2.
The Tracking Layer is intended to provide global “stereo” coverage for missile defense, replacing legacy systems like SBIRS with a more resilient, proliferated mesh network by the end of the decade.