WASHINGTON, D.C. — On Thursday, January 15, 2026, Hydrosat announced the closing of a €51 million ($60 million) Series B funding round. The capital is designated to accelerate the global deployment of the company’s thermal infrared satellite constellation and its AI-driven geospatial analytics platform.
Capital to Combat Global Water Stress
The investment round was led by Hartree Partners, Subutai Capital Partners, and Space 4 Earth, with new participation from Truffle Capital and follow-on support from the Luxembourg Future Fund, OTB Ventures, and Statkraft Ventures. The funding follows an increase in demand for “decision-grade” thermal data as climate change intensifies water scarcity and agricultural volatility. Hydrosat currently serves a range of high-stakes clients, including the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The company previously secured a NOAA grant in early 2024 and has active contracts with the U.S. Air Force to improve weather modeling for national defense.
Expanding High-Frequency Thermal Collection
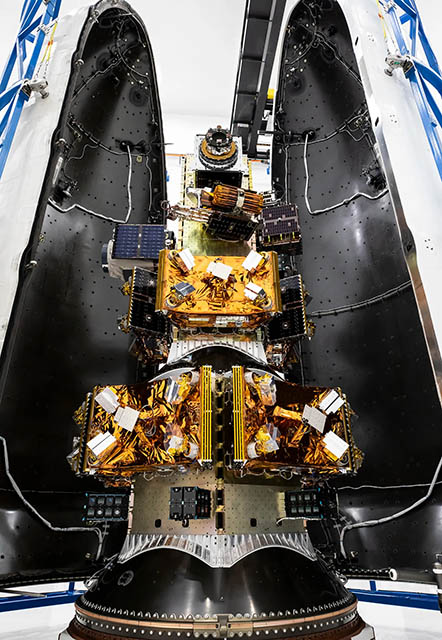
Hydrosat currently operates two thermal infrared satellites on-orbit, providing a daily collection capacity of more than 10 million square kilometers of imagery. Unlike traditional Earth observation data, which can be infrequent or low-resolution, Hydrosat’s sensors deliver high-frequency, field-level insights into soil moisture, crop health, and surface temperature. These data sets are processed through proprietary machine learning models to provide predictive analytics for agribusinesses and government agencies. This operational capacity was bolstered by the company’s 2023 acquisition of IrriWatch, which integrated advanced irrigation management software into the Hydrosat ecosystem.
Global Footprint and Workforce Growth
With the close of this Series B, which follows a $20 million funding round in 2023, the company plans to deepen its presence in key regions including the Middle East and North Africa (MENA), Central Asia, India, and Latin America. Additionally, Hydrosat intends to double its workforce of remote sensing and machine learning specialists at its Luxembourg headquarters by the end of 2026 to support its next phase of constellation development.